What is the resistance of a refrigerator's defrost heater?
Discover what a defrost heater is in a refrigerator, how it works to maintain optimal cold, and learn how to measure its resistance in ohms with a multimeter…

The defrost heater is an essential component in modern refrigerators, especially frost-free models, as it prevents excessive ice buildup that can affect the appliance's performance. This heater warms the evaporator to melt the ice that forms, ensuring efficient and even cooling inside the refrigerator. Knowing the defrost heater's resistance (in ohms) is key to diagnosing whether it's functioning correctly and maintaining the refrigerator in optimal condition.
Besides extending the appliance's lifespan, a properly functioning defrost heater helps preserve food in better condition by preventing temperature fluctuations and humidity problems. Therefore, understanding how to test it with a multimeter and recognizing its typical readings is a practical skill for anyone who wants to keep their refrigerator in good working order.
Definition and function of the defrost heater
The defrost heater is an electric heating element installed in the refrigerator's evaporator to melt accumulated ice. When the system detects frost buildup, this heater activates to warm the evaporator and prevent ice from blocking the flow of cold air. As a writer with experience in appliance maintenance, I can confirm that a properly functioning defrost heater is essential for the refrigerator to operate correctly and prevent problems such as poor air circulation or premature compressor wear.
This component is especially important in No Frost systems, where the goal is to prevent visible ice buildup in the freezer and maintain a constant temperature throughout the refrigerator.
Common signs or symptoms
- Ice on the evaporator: indicates that the defrost heater is not melting the frost properly, which can block airflow and reduce cooling.
- Not very cold at the bottom of the refrigerator: this is usually due to an evaporator covered in ice that prevents the cold air from being distributed properly.
- Fan blocked by ice: The fan may stop or malfunction if it is obstructed by frost, resulting in noise and poor air circulation.
- Leaks inside or outside the refrigerator: melted frost can accumulate and drip if the defrost system fails.
- Excessive frost: visible accumulation of ice on walls or trays, a clear symptom that the heating element is not fulfilling its function.
Common causes
Cause 1: Damaged defrost heater
The resistor can burn out or break due to wear and tear or short circuits. This can be detected by measuring its electrical resistance with a multimeter; if the value is outside the typical range, it is damaged.
Cause 2: Defective bimetal or defrost thermostat
This component controls when the heating element activates. If it fails, the element may not receive power to heat. It can be detected by measuring continuity or checking the defrost cycle.
Cause 3: Evaporator temperature sensor
The sensor sends the signal to activate the defrost cycle. If it's broken or out of range, the system won't work properly. You can check it with a multimeter or by temporarily replacing it.
Cause 4: Timer or electronic board
They control the defrost cycles. If they are faulty, they won't activate the heating element. They are detected through functional tests or more advanced diagnostics.
Cause 5: Burned-out thermal fuse
It protects the resistor from overheating. If it's open, it cuts off the current to the resistor. It can be checked with a multimeter in continuity mode.
Step-by-step (safe) solutions
Before taking any measurements or performing any repairs, disconnect the refrigerator from the electrical supply to avoid accidents.
- Step 1: Locate the defrost heater. In No Frost models, it's located in the evaporator, usually behind a rear cover in the freezer. You'll need a screwdriver and a multimeter.
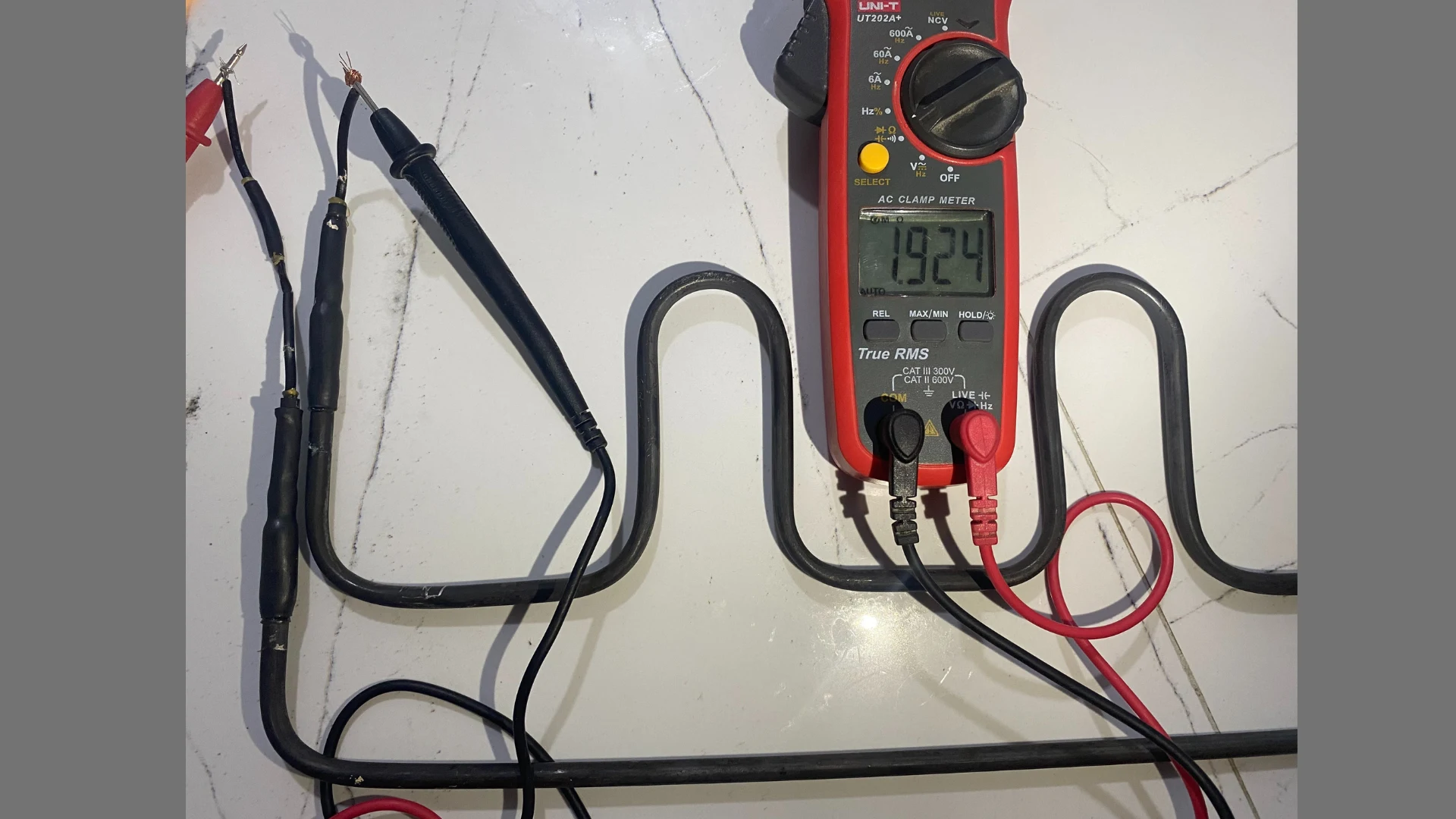
- Step 2: Disconnect the resistor wires and set the multimeter to ohms (Ω) mode. Measure the resistance between the terminals. A value within the typical range indicates that the resistor is good.
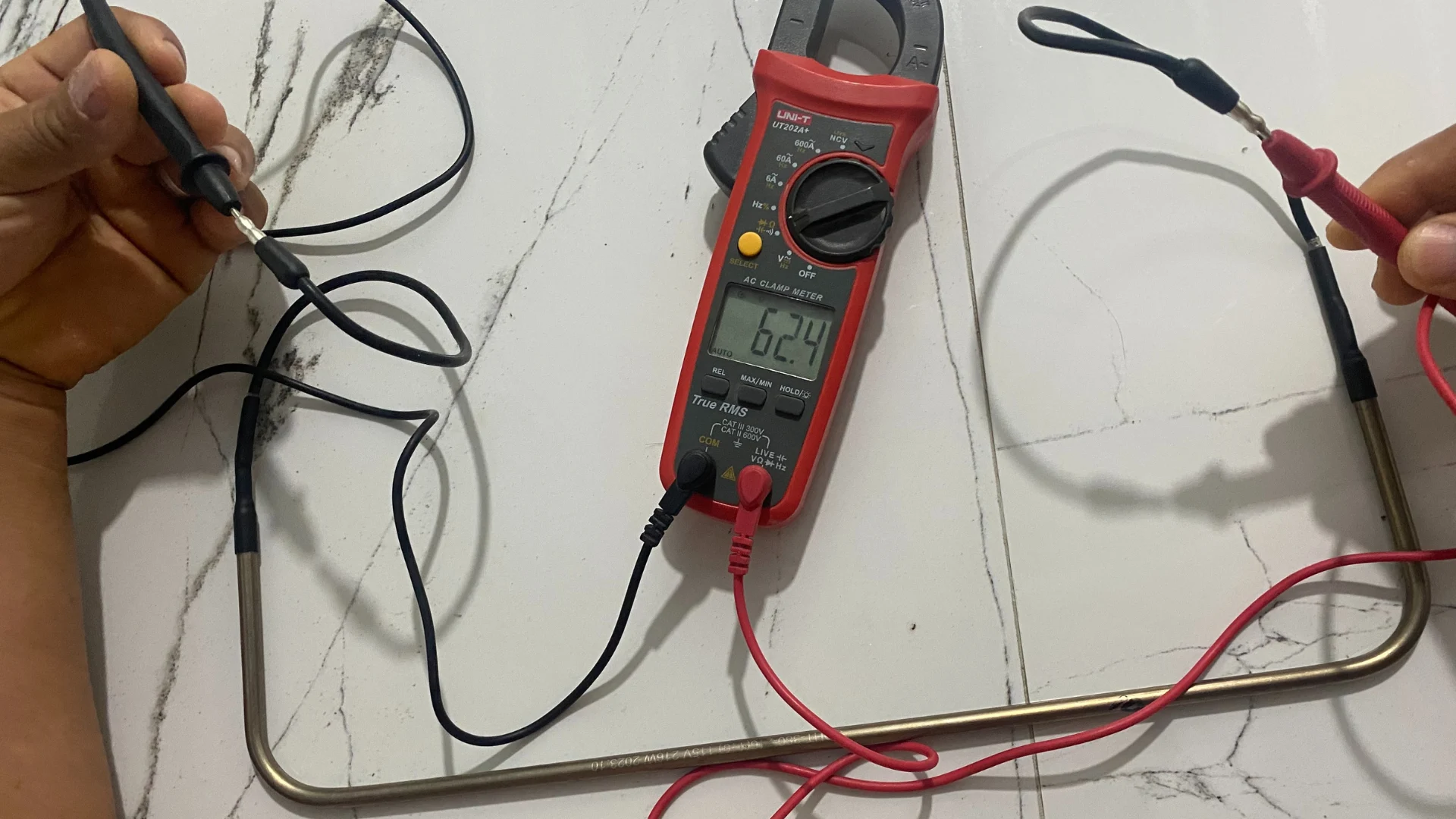

- Step 3: If the value is out of range or open (infinite), it's time to replace the resistor. If you are unsure or inexperienced, stop the process and contact a certified professional.
Quick alternatives
- Option A: Manually defrost the evaporator to temporarily alleviate the problem. Pros: Quick and easy. Cons: It doesn't solve the underlying problem and is only a temporary fix.
- Option B: Reset the timer or electronic board if the equipment allows it. Pros: Can reset cycles. Cons: Requires technical knowledge and is not always effective.
Costs and when to call a technician
The cost of replacing a defrost heater ranges from $20 to $80 USD, depending on the brand, model, and place of purchase. Factors that influence the price include voltage, wattage, size, and connector type.
You should call a technician if, after measuring the resistance and other components, you cannot identify the problem, if the electronic board or timer is failing, or if you do not have the tools or experience to work with electricity.
Common mistakes to avoid
- Measuring resistance without disconnecting the refrigerator from the electrical supply is dangerous.
- To avoid confusing the resistor with other components, check the manual or label to identify it correctly.
- Buying a replacement part that is incompatible in voltage or power can damage the equipment or cause it to malfunction.
Preventive maintenance (checklist)
- Check the defrost heater every 6 months for wear.
- Clean the evaporator and ventilation area every 3 months to prevent ice buildup.
- Verify the correct functioning of the timer or electronic board annually.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a normal resistance range for the defrost heater? The typical range is between 20 and 120 ohms, depending on the power and voltage.
Can a resistor of a different wattage be used? It is not recommended, as it may cause malfunction or damage.
What happens if the defrost heater doesn't work? Ice builds up on the evaporator, reducing cooling and potentially damaging other components.
Resources and references
- Whirlpool Official Service Manual
- Samsung technical diagnostic guide for No Frost systems.
Conclusion
The defrost heater is vital for your refrigerator to maintain proper cooling and prevent ice buildup. Knowing its resistance (in ohms) and how to test it with a multimeter will allow you to diagnose problems early and make informed decisions about repairs or maintenance. If you have any doubts or find readings outside the acceptable range, don't hesitate to contact a qualified technician to ensure your appliance is working correctly. Keep your refrigerator in top condition and protect your food today!